The penis is as complicated as the other organs of the human body, despite a deceptively simple look. Moreover, since the 2 functions of the penis are well-known to males and females alike, there's a tendency to assume that everyone is aware of everything worth knowing regarding it.
However, there are continuously some queries left unrevealed or some obscure bit of information that no-one bothers to recall and which can become fascinating in a specific context.
thus here’s a general description of the penis whose aim is to produce a comprehensive presentation of this organ.
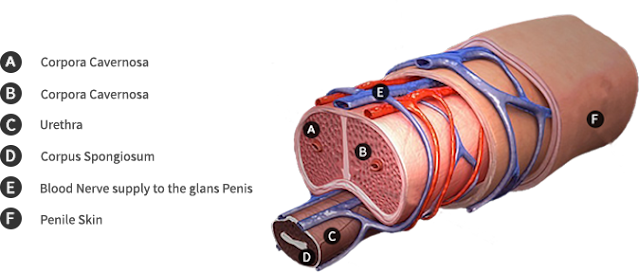
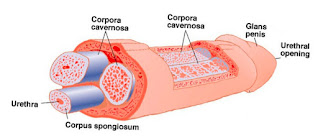
Basically, the human penis is formed of 2 parts: the shaft and also the glans (also called the head).
The shaft isn't a muscle as some have thought. it's formed of 3 columns of tissue, one among which continues forward to make the glans. The 3 columns are known as Corpus Spongiosus, that forms the bottom of the penis and also the glans, and Corpora Cavernosa, that are 2 sections of tissue situated next to each other on the top side of the penis.
The shaft is covered in skin, whereas the glans supports the loosely connected fold of skin called the foreskin. The foreskin is connected to the bottom of the penis, in a region known as the frenum. And, lastly, the urethra is travelling through the penis from one end to the other. This canal is a passage for both urine, collected within the bladder, and also the sperms, made within the testicles.
Erection is achieved by filling the 2 Corpora Cavernosa with blood. in contrast to some other mammals, humans don't have any erectile bone and need to depend instead on engorgement with blood to achieve erection.
once the erection is triggered by sexual stimulation, the arteries that bring blood to the erectile organ dilate so as to increase blood flow. The sponge-like Corpora Cavernosa fills up with blood, that makes the penis stiff. The stiffer tissues constrict the veins that carry blood far from the penis so as to keep up the erection.
Each male baby is born with a full set of reproductive organs. However, these organs aren't totally developed and remain so till the boy enters puberty.
At puberty, typically between the ages of ten and fourteen, the pituitary gland starts secreting hormones that induce the testicles to provide testosterone. Testosterone is the androgen hormone that controls all the physical and lots of of the psychological traits that define man.
Its presence ensures the development of larger bones and bigger muscle mass in men. it's additionally responsible for the rise in penis and testicles sizes, the manifestation of pubic hair and also the deeper tone of the male voice.
The penis stops growing at the end of puberty, that comes round the age of eighteen. However, there are several environmental factors which will delay or accelerate the onset or the end of puberty. this means that some men might experience penis growth beyond the age of eighteen.
a common urban myth that nearly anyone has heard of is that the concept that penis size is linked to the size of another parts of the body. the most common versions of this myth concentrate on the size of hands, feet, nose or overall height to determine the size of the penis.
Actually, there's no such link. though the development of the penis in the embryo is controlled by a similar genes as the limbs, penis growth at puberty is entirely ruled by the androgenic hormone ( testosterone) and has no relationship to any of the other parts of the body.
Some men are born with huge penises. this is often an undisputed reality of life whose causes are still a mystery to science.
As expressed above, there's no correlation between penis and body size. Studies conducted on bats have shown that the sexual organs and the brain need massive quantities of energy to develop.
At some point, the developing embryo decides whether it desires a much bigger brain or a much bigger set of sexual organs. However, science remains at a loss to know how the choice is made and why.